5th day in hospital~
2day i've stay in emergency department until 1pm only ..after that i went to surgical department~1st time enter to operation theatre~c appendix removal...cool men~ then i jz knew a Ho..then she ask me to eat lunch with her~
she talk all the story about Ho..how;s bad n terrible is their life..skipping lunch everyday ,sleeping not more than 3 hours a day..even sumtime didnt sleep when they on call.. kind of sad life xia~summore they nid to exam every 2 months..once fail they nid to work in the same department for 3 months.which means they nid to extend their ho life..
evry 4 months they nid to change department~
each department they nid to exam..more on knowledge..
so..after they work..they went back home still nid to study..dun haf time to sleep.
so..her feeling after graduate is lifeless!!hahaha..
n the responsible bcome big dy..their job is about life n death .. cannot do silly mistakes.
k..back to the topic..5th day in hospital
so my first patient~
one old chinese man motor accident due to feel sudden diziness and fall down .
then..his leg has type IIIB open fracture ,which cause unstoppable bleeding and sever contaminated and loss of tissue
come let's c bone fracture..
what type and cause there is in bone fracture?
so..bone fracture can be cause by traumatic(accident) and physiology(old).
here;s some type of fracture which i get it from the thefreedict.com and wikipedia.,
Fracture: breaking of one part especially bone.










she talk all the story about Ho..how;s bad n terrible is their life..skipping lunch everyday ,sleeping not more than 3 hours a day..even sumtime didnt sleep when they on call.. kind of sad life xia~summore they nid to exam every 2 months..once fail they nid to work in the same department for 3 months.which means they nid to extend their ho life..
evry 4 months they nid to change department~
each department they nid to exam..more on knowledge..
so..after they work..they went back home still nid to study..dun haf time to sleep.
so..her feeling after graduate is lifeless!!hahaha..
n the responsible bcome big dy..their job is about life n death .. cannot do silly mistakes.
k..back to the topic..5th day in hospital
so my first patient~
one old chinese man motor accident due to feel sudden diziness and fall down .
then..his leg has type IIIB open fracture ,which cause unstoppable bleeding and sever contaminated and loss of tissue
come let's c bone fracture..
what type and cause there is in bone fracture?
so..bone fracture can be cause by traumatic(accident) and physiology(old).
here;s some type of fracture which i get it from the thefreedict.com and wikipedia.,
Fracture: breaking of one part especially bone.
Treatment. Immediate first aid consists of splinting the bone with no attempt to reduce the fracture; it should be splinted “as it lies,” which means supporting it in such a way that the injured part will remain steady and will resist jarring if the victim is moved. Later it will be treated by reduction, which means that the broken ends are pulled into alignment and the continuity of the bone is established so that healing can take place. Fracture healing is truly a process of regeneration. Fractures heal with normal bone, not with scar tissue. Closed reduction is performed by manual manipulation of the fractured bone so that the fragments are brought into proper alignment; no surgical incision is made. Open fractures are highly contaminated and must be débrided and copiously irrigated in the operating room. A fracture may also require internal fixation with pins, nails, metal plates, or screws to stabilize the alignment. Once closed reduction is accomplished, the bone is immobilized by application of a cast or by an apparatus exerting tractionon the distal end of the bone.

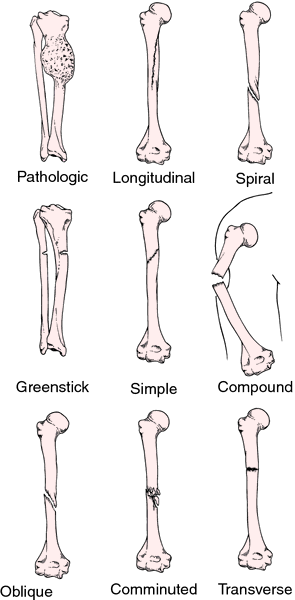
All fractures can be broadly described as:
- Closed (simple) fractures: are those in which the skin is intact
- Open (compound) fractures: involve wounds that communicate with the fracture, or where fracture hematoma is exposed, and may thus expose bone to contamination. Open injuries carry a higher risk of infection.
Other considerations in fracture care are displacement (fracture gap) and angulation. If angulation or displacement is large, reduction (manipulation) of the bone may be required and, in adults, frequently requires surgical care. These injuries may take longer to heal than injuries without displacement or angulation.
- Compression fractures: usually occurs in the vertebrae, for example when the front portion of a vertebra in the spine collapses due to osteoporosis (a medical condition which causes bones to become brittle and susceptible to fracture, with or without trauma).
Other types of fracture are:
- Complete fracture: A fracture in which bone fragments separate completely.
- Incomplete fracture: A fracture in which the bone fragments are still partially joined. In such cases, there is a crack in the osseous tissue that does not completely traverse the width of the bone.[1]
- Linear fracture: A fracture that is parallel to the bone's long axis.
- Transverse fracture: A fracture that is at a right angle to the bone's long axis.
- Oblique fracture: A fracture that is diagonal to a bone's long axis.
- Spiral fracture: A fracture where at least one part of the bone has been twisted.
- Comminuted fracture: A fracture in which the bone has broken into a number of pieces.
- Impacted fracture: A fracture caused when bone fragments are driven into each other.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
LET's look at Open fracture..
LET's look at Open fracture..
there;s feel type of open fracture actually,
type 1 open fracture- fracture with minimun wound of 1cm,without contamination and minimal injury of soft tissue.


type II open fracture
wound between 1 and 10cm,mild contamination,extensive soft tissue damage and minimal to moderate crushing component.


Type IIIA fracture.
wound with minimum 10cm.severe contamination and severe crushing component


Type IIIB fracture. wound larger than 10cm .severe contamination ,severe crushing component and severe loss of tissue


Type IIIC fracture.
wound larger than 10cm,severe contamination ,and injury of neurovovascular.


Comments
Post a Comment