Biochem usmle road map
normally i will see from glycogenolysis(break down of glycogen) and glycogenesis(formation of glycogen),which start frm glycogen top down to the acetylcoA right before kreb's cycle.
In glycogenolysis. Enzyme that u must remember glycogen phosphorylase(and debranching enzyme) to form glucose 1 P and glycogen synthase with branching enzyme.what so important about this enzyme? use this mneumonics.
Glycogen storage disease:
we(V) Prepare Costumes And Marry Her
ABCD
Anderson-Branching
Cori -Debranching
I-Von gierke
-glucose 6 phosphatase- severe hypoglycemia,lactic acidosis,hepatomegaly,hyperlipidemia,hyperuricemia,short stature doll like facies,protruding abdomen emaciated extremities.
II- Pompe
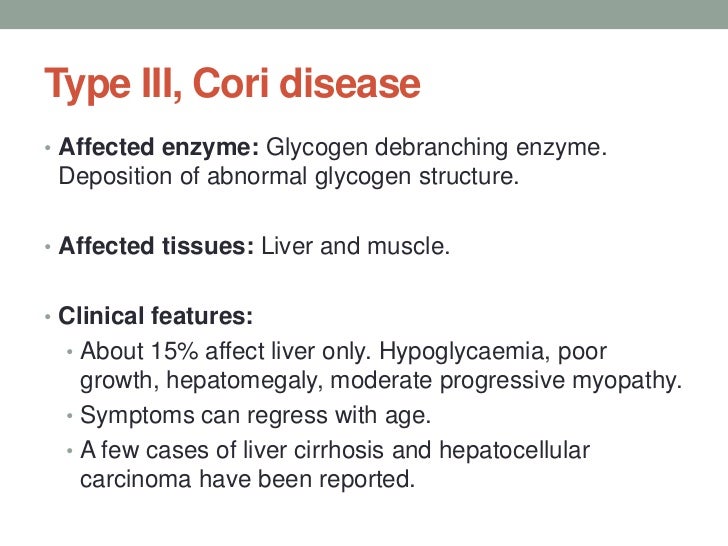
III- Cori-debranching enzyme
IV- Anderson
V- Mcardle-Muscle glycogen phosphorylse
VI- Hers-Hepatic glycogen phosphorylase
mild fasting hypoglycemia hepatomegay cirrhosis
SUmmary:
In glycogenolysis. Enzyme that u must remember glycogen phosphorylase(and debranching enzyme) to form glucose 1 P and glycogen synthase with branching enzyme.what so important about this enzyme? use this mneumonics.
Glycogen storage disease:
we(V) Prepare Costumes And Marry Her
ABCD
Anderson-Branching
Cori -Debranching
I-Von gierke
-glucose 6 phosphatase- severe hypoglycemia,lactic acidosis,hepatomegaly,hyperlipidemia,hyperuricemia,short stature doll like facies,protruding abdomen emaciated extremities.
autosomal recessive
Clinical manifestations result, directly or indirectly, from
- inability to maintain an adequate blood glucose level during the post-absorptive hours of each day;
- organ changes due to glycogen accumulation;
- excessive lactic acid generation;
- damage to tissue from hyperuricemia;
- in GSD Ib, bleeding and infection risk from blood cell effects.
II- Pompe
- The disease is caused by a mutation in a gene (acid alpha-glucosidase: also known as acid maltase) on long arm of chromosome 17 at 17q25.2-q25.3 (base pair 75,689,876 to 75,708,272)
- The infantile form usually comes to medical attention within the first few months of life. The usual presenting features are cardiomegaly (92%),hypotonia (88%),cardiomyopathy(88%), respiratory distress (78%), muscle weakness (63%), feeding difficulties (57%) and failure to thrive (50%).
- The main clinical findings include floppy baby appearance, delayed motor milestones and feeding difficulties. Moderate hepatomegaly may be present. Facial features include macroglossia, wide open mouth wide open eyes, nasal flaring (due to respiratory distress), and poor facial muscle tone. Cardiopulmonary involvement is manifest by increased respiratory rate, use of accessory muscles for respiration, recurrent chest infections, decreased air entry in the left lower zone (due to cardiomegaly), arrhythmias and evidence of heart failure.
- Median age at death in untreated cases is 8.7 months and is usually due to cardiorespiratory failure
III- Cori-debranching enzyme
IV- Anderson
- Branching enzyme deficient
V- Mcardle-Muscle glycogen phosphorylse
- muscle cramp n weakness on exercise
VI- Hers-Hepatic glycogen phosphorylase
mild fasting hypoglycemia hepatomegay cirrhosis
SUmmary:
.JPG)



Comments
Post a Comment